FOLLOW US

What is artificial intelligence (AI)? Learn about AI
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a field of technology that focuses on creating machines and computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These functions include learning, reasoning, problem solving, perception, understanding language, and decision making.
AI systems use various techniques, such as machine learning and deep learning, to analyze data, identify patterns, and make decisions. AI is integrated into many applications and devices, allowing them to recognize objects, understand human language, learn from experience and operate independently.
Generative AI, a significant area of recent focus, involves generating original content such as text, images, and video. It builds on technologies like machine learning and deep learning, using models like neural networks to simulate complex decision-making processes like the human brain.
AI offers many benefits, including automation of repetitive tasks, improved decision making, reduction of human error and increased efficiency in various industries. However, it also presents challenges and risks related to data protection, model integrity, operational management and ethical considerations.
How does AI work?
Artificial intelligence (AI) works through a systematic series of steps designed to mimic human-like decision-making processes. There are several important things you need to determine in order to create an AI. Identify and define problems, determine desired outcomes, organize and manage data sets, select the most appropriate technology, and rigorously test potential solutions. If the original solution fails to meet expectations, you can continue to experiment to achieve the desired results.
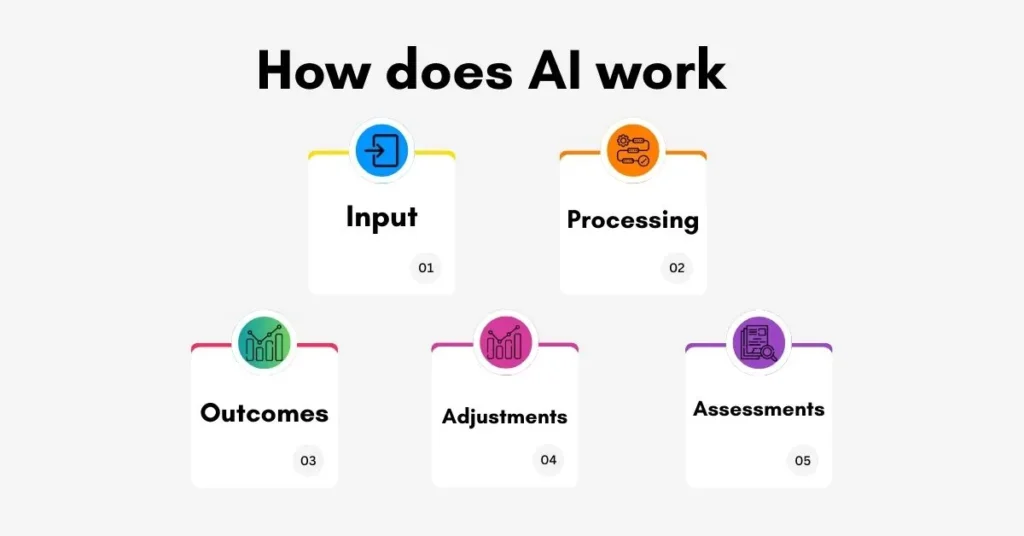
Below, to explain how AI works, I’ll mention five steps: input, processing, output, coordination, and evaluation.
Input
The first phase involves gathering large amounts of data from various sources including text, audio, video and other formats. This data is carefully classified into segments that can be effectively processed by algorithms and those that cannot. Establishing a protocol and defining criteria for processing must determine which data will be used to achieve specific results.
Processing
Once the data is collected and systematically inputted, the next step involves enabling AI to make decisions based on the data. At this stage, the AI employs advanced algorithms to sort and decipher the data to identify patterns that it has been programmed to recognize. AI systems constantly filter incoming data, looking for similar patterns that align with previously learned information. This ability to identify patterns is critical to transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Outcomes
Following the processing stage, AI uses these complex patterns to predict potential outcomes related to customer behavior and market trends. In this step, the AI is programmed to evaluate whether certain data instances are a “pass” or “fail”. Basically determining whether they align with established patterns. This assessment is essential in generating results that inform the decision-making process across a variety of applications.
Adjustments
In situations where data sets are considered “failed”, AI systems learn from these inconsistencies, repeating the process in different scenarios. This may involve adjusting the parameters of the algorithm to better accommodate the unique characteristics of the data set or making minor changes to the algorithm itself. At this stage, the resulting step may need to be revised to ensure alignment with the conditions and requirements of the current data set.
Assessments
AI’s task completion step is evaluation. At this point, AI synthesizes insights from data sets to make predictions based on previous results and necessary adjustments. Feedback from these adjustments is incorporated back into the algorithm to improve future performance. This continuous feedback loop allows AI systems to evolve and improve over time, ensuring more accurate and reliable results on subsequent tasks.
AI use cases
AI has many real-world applications. Here is just a small sample of some uses to illustrate its potential in various industries:
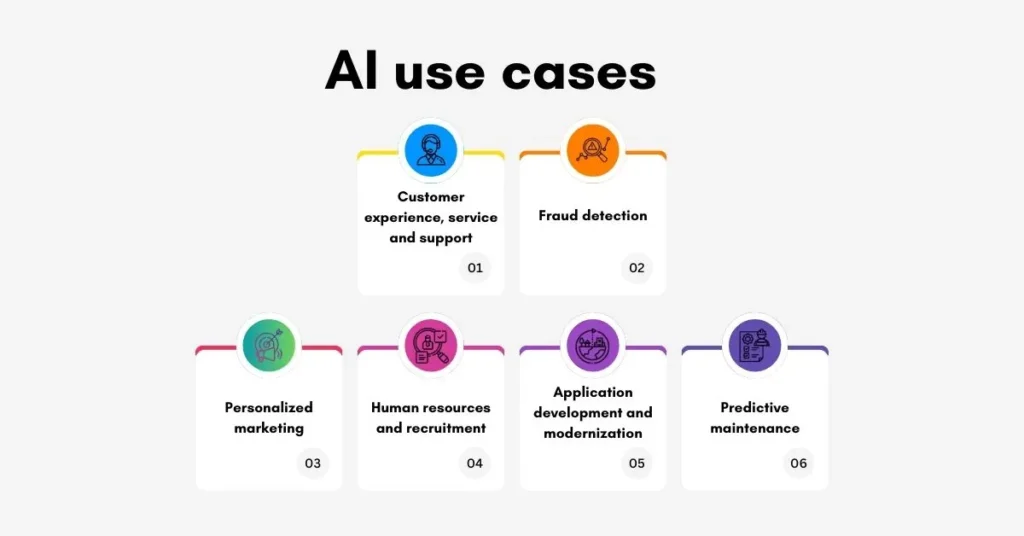
Customer experience, service and support
Companies can implement AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to efficiently manage a wide range of customer inquiries, support tickets and other interactions. These advanced tools use state-of-the-art natural language processing (NLP) and generative AI capabilities to accurately understand and answer customer queries regarding order status, product details, return policies and more. By doing so, they enhance the overall customer experience.
Chatbots and virtual assistants are able to offer businesses always-on one-on-one support. To ensure that customers get support at any time of the day They provide quick answers to frequently asked questions (FAQs), significantly reducing waiting time for customers.
Fraud detection
Machine learning and deep learning algorithms have the ability to analyze large amounts of transactional data, detect patterns and flag anomalous activities that deviate from the norm. These anomalies may include unusual spending behavior, unexpected login locations, or other irregularities that may suggest fraudulent transactions.
This proactive approach not only helps reduce the impact of fraudulent activities but also improves the organization’s security framework. As a result, this provides both organizations and their customers with a greater sense of security and peace of mind, knowing that any suspicious activity is being monitored and addressed immediately.
Personalized marketing
Retailers, banks and various other customer-facing organizations have the opportunity to leverage artificial intelligence to create highly personalized customer experiences and marketing campaigns that only delight customers. Not only engages but also significantly improves sales and prevents customer churn. Using data derived from customer purchase history and behavior, sophisticated deep learning algorithms are able to recommend products and services that customers want most.
These algorithms can even generate personalized copy and special offers that are specifically tailored to individual customers in real-time, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Human resources and recruitment
AI-powered recruiting platforms offer transformative approaches by increasing efficiency and effectiveness. Using advanced algorithms and machine learning, they screen resumes and select qualified candidates. Besides, they match candidates with skills and experience and facilitate initial interviews through video analysis.
These innovative tools streamline recruitment workflows and reduce administrative burdens. As a result, recruiting teams can focus on strategic decisions. By shortening response times and reducing hiring time, platforms enhance the candidate experience. AI-powered recruitment platforms are making processes more efficient and candidate-friendly.
Application development and modernization
Generative AI code generation tools and automation tools can significantly streamline various repetitive coding tasks typically associated with application development. They have the ability to accelerate the entire process of migration and modernization, including reconfiguration and re platforming of legacy applications at an unprecedented scale.
Using these advanced tools, developers can speed up numerous tasks, increase code consistency, and reduce the likelihood of errors. This not only improves efficiency but also allows developers to focus more on innovation and less on the mundane aspects of coding. Furthermore, these tools are helpful in maintaining high-quality code standards throughout the development lifecycle.
Predictive maintenance
Machine learning models have the ability to thoroughly analyze large amounts of data collected from various sources such as sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and operational technology (OT). By doing so, they can accurately predict when maintenance will be needed and predict potential equipment failures well before they actually occur.
This AI-powered preventive maintenance strategy not only helps prevent unexpected downtime but also empowers businesses to anticipate potential supply chain issues long before they have a chance to impact their bottom line. With machine learning at the forefront, organizations can increase their performance and ensure that all systems are running smoothly, thereby protecting their productivity and profitability.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence?
AI technologies, especially advanced deep learning models such as artificial neural networks, have revolutionized data management. These systems are able to process vast amounts of information and make predictions faster and more accurately than humans. AI applications can quickly analyze data and transform it into actionable insights.
A major disadvantage of AI is the high cost of processing huge data, which increases business costs. The increasing incorporation of AI requires organizations to be careful to avoid developing discriminatory systems.
Advantages of AI
Some of the benefits of AI are given below:
1. Detail-oriented job excellence is an important aspect that can significantly increase work quality and efficiency. AI technology is an exceptional fit for tasks that require vigilance. Because it is able to identify subtle patterns and complex relationships in large amounts of data that can easily be overlooked by humans.
In oncology, AI systems have shown remarkable accuracy in early-stage cancer detection. These identify early signs of breast cancer and melanoma, highlighting them for evaluation by healthcare professionals. Thus, AI aids in early diagnosis and helps doctors make informed decisions, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
2. Data-heavy work skills are critical in today’s fast-paced world, where large amounts of information are being generated and analyzed. AI and automation tools have reduced data processing time, transforming the way organizations work. It is particularly useful in sectors such as finance, insurance and healthcare, which involve routine data entry and analysis and data-driven decision making. Through automation, businesses can increase productivity and accuracy.
In banking and finance, AI models process data quickly and accurately to predict market trends and analyze investment risks. It helps financial institutions to make informed decisions and reduce risk. In insurance, AI improves efficiency in claims processing and fraud detection. In healthcare, AI aids in diagnosis, patient records and personalized treatment plans, which ensure better patient outcomes.
3. Time savings and productivity gains are significant benefits due to advances in AI and robotics. These technologies not only have the ability to automate various operations but also significantly improve security measures and increase efficiency levels.
AI-powered robots are becoming increasingly common, taking over dangerous or repetitive tasks in warehouse automation. It helps human workers focus on critical tasks by reducing risk, thereby increasing productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
4. AI tools are efficient in massive data processing using artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze results. They are able to adapt to new information and situations through continuous learning and improvement.
AI applications have shown their potential by demonstrating reliable results in complex tasks, such as legal document review and language translation, where accuracy and context are important. These tools ensure reliable and quality results by increasing productivity.
5. Customization and personalization are two key elements that significantly enhance the user experience of e-commerce platforms by delivering interaction and content across various digital platforms.
Advanced AI models analyze user behavior and preferences to recommend personalized products, which enhance the shopping experience and customer satisfaction, and make interactions more intuitive and user-friendly.
6. Round-the-clock availability is the big advantage of AI technology. AI programs don’t need sleep or rest, so they can work without downtime. For example, AI-powered virtual assistants can provide 24/7 customer service.
This capability is especially beneficial for businesses with high customer interaction, as it ensures that queries are resolved quickly at any time of the day or night. By maintaining consistent availability, these AI systems increase customer satisfaction by improving response times.
7. Scalability is an important feature of AI systems, as it enables the handling of increasing amounts of work and data. This scalability makes artificial intelligence suitable where data and workloads can grow rapidly.
These scenarios include Internet search engines and business analytics, where companies process and analyze large amounts of data to gain insights and make decisions.
8. Accelerated research and development is a transformative force in today’s scientific field. AI can accelerate R&D efforts in pharmaceuticals and materials science, helping researchers discover new drugs, materials or compounds by simulating, modeling and analyzing situations quickly.
This acceleration increases efficiency and opens up new possibilities for innovation, enabling unimaginable breakthroughs. Researchers can explore complex hypotheses, optimize experimental designs, and predict results quickly and accurately, revolutionizing scientific inquiry and discovery.
9. Sustainability and conservation are important issues in today’s world. AI and machine learning are being used in environmental change, weather forecasting and management of conservation initiatives. Machine learning analyzes satellite imagery and sensor data through advanced algorithms and data-processing to determine wildfire risk, pollution monitoring and endangered species populations.
These technologies detect patterns and trends that are not possible for humans, providing environmental insights. Integrating AI into sustainability creates efficient strategies to conserve biodiversity while minimizing environmental impact. These tools aid in real-time monitoring and long-term planning and decision-making in conservation efforts.
10. AI technology in process optimization enhances efficiency in various industries, streamlining and automating complex processes. It reduces operational costs by increasing productivity. For example, in the manufacturing sector, AI models analyze workflows to identify inefficiencies and predict potential bottlenecks, ensuring smooth production lines.
In the energy sector, AI predicts electricity demand patterns and optimizes energy supply, ensuring stable distribution. It is revolutionizing the industry by helping to respond quickly to demand fluctuations, providing innovative solutions in process optimization, driving growth and driving sustainability.
Disadvantages of AI
The following are some disadvantages of AI:
1. AI development is expensive, resource-intensive and requires significant financial investment and technological infrastructure. Model building requires upfront investment in infrastructure, computational resources, specialized software, and secure storage of massive training data. After initial training, there are ongoing costs of model estimation, fine-tuning and retraining to maintain system accuracy.
AI incurs constant costs to keep updated with the latest data and computational advances, which rapidly increases costs for generative AI applications. For example, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman reported that training the GPT-4 model cost more than $100 million, highlighting the challenges organizations face in developing cutting-edge AI technologies.
2. Developing, operating and troubleshooting AI systems demands technical skills and specialized knowledge, which are different from skills for developing non-AI software. Building and deploying machine learning applications is a complex, multidimensional process.
This process includes dataset collection, cleaning and organizing, algorithm selection, parameter tuning, and model testing. Each of these steps needs to be carefully understood and executed to ensure proper and efficient functioning of the AI system.
3. Lack of talent A shortage of fully trained professionals in AI and machine learning adds to the technical complexity. The increasing demand for these skills in various industries has made this problem challenging.
Due to AI talent shortages and demand gaps, many organizations are struggling to find enough qualified staff for AI projects, which can hinder project progress and implementation and affect innovation and competitiveness.
4. Algorithmic bias is a major problem in artificial intelligence and machine learning. These algorithms reflect biases in the training data, which can be a significant problem when AI systems are implemented on a large scale. The bias inherent in the data may be greater than just replication. In some cases, the AI system encodes subtle biases, which seem intentional and powerful, perpetuating the problem.
The example of Amazon’s AI-powered recruitment tool showed that it favored male candidates, a reflection of the tech industry’s gender imbalance. This case warns of the potential for inadvertent amplification of AI systems.
5. Job displacement is becoming a major problem as a result of advances in artificial intelligence. If companies replace humans with machines and automated systems, AI could lead to job losses. As the power of AI models increases, companies seek to automate workflows and reduce costs.
Some copywriters report being replaced by LLMs like ChatGPT, which can produce text quickly and efficiently. The potential for AI to replace human roles is affecting copywriting, customer service, data analytics, and certain aspects of healthcare and manufacturing.
6. Security vulnerability of AI systems is a major concern due to cyber threats. With data poisoning and adversarial machine learning attacks, malicious actors can leak confidential information and produce misleading or harmful output.
This issue is particularly worrisome in sectors such as financial services, government operations, healthcare and critical infrastructure, where the potential for catastrophic consequences highlights the need for increased protection and robust defenses against vulnerabilities in AI systems.
7. Environmental influences are important during the advancement of artificial intelligence. Data centers and network infrastructures use a lot of energy and water for AI models, which require constant cooling and maintenance. As a result, the training and use of AI models has a profound impact on the environment.
AI’s carbon footprint, especially for large generative models, requires more computing resources. Increased energy demand during training and exercise increases carbon emissions. As AI technology advances, it is important to address its environmental impact to ensure sustainable development.
8. The legal issues surrounding artificial intelligence are complex, raising questions of privacy and liability. Analyzing personal data and making decisions through AI technology has serious privacy implications. There are concerns about the methods of collection, storage and use of personal information and the adequacy of data protection laws.
Courts and legal systems have not yet clarified how authorship and ownership of material created by LLMs will be determined. AI-generated content can blur the boundaries between original and derivative works, raising questions about intellectual property rights. Legal challenges may become apparent as AI technology advances, requiring adaptation of legal frameworks to protect innovation and individuals’ rights.
Why is AI important?
AI is changing the way we live, work and play sports. It is being used in the business world to automate tasks like customer service, lead generation, fraud detection and quality control. By automating these processes, businesses can increase efficiency, reduce costs and improve accuracy.
Artificial intelligence (AI) in various industries performs tasks with efficiency and precision, often exceeding human capabilities. Especially in tasks requiring repetition and attention to detail, such as analyzing huge legal documents, AI ensures that all relevant fields are filled in correctly and that no important information is overlooked.
AI data processing capabilities give enterprises deep insights, which elude human analysts. The rapid expansion of generative AI tools with innovative solutions and transformation of traditional methods is increasingly important in education, marketing, product design and more.
Advances in AI techniques have led to an explosion of efficiency in various sectors and opened up new business opportunities. For example, Uber became a Fortune 500 company by connecting taxis with riders using advanced software, revolutionizing the transportation industry. The impact of AI extends beyond transportation.
It helps healthcare, finance, manufacturing and retailers optimize processes, predict trends and enhance customer experience. As AI evolves rapidly, it will reshape the economy, creating challenges and opportunities for businesses worldwide. The potential for innovation and growth is immense, as AI technology permeates everyday operations and forces companies to adopt new strategies.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is now an essential part of the strategic operations of the world’s largest and most prosperous companies. Tech giants such as Alphabet, Apple, Microsoft and Meta use AI to increase efficiency, innovate products and maintain a competitive edge.
AI plays an important role in enhancing the capabilities and performance of Google’s search engine, which is more intuitive and efficient for users. Waymo, Alphabet’s self-driving car company, is an example of AI’s impact on transportation technology. In addition, the Google Brain research lab has played a leading role in the development of the Transformer architecture, which is the foundation of NLP advancements.
The 4 Types of AI
Researchers are seeking to develop more advanced artificial intelligence as well as a more nuanced explanation of intelligence and consciousness. To lay the theoretical and practical foundations for the advancement of AI technology, scholars have identified four types of artificial intelligence.
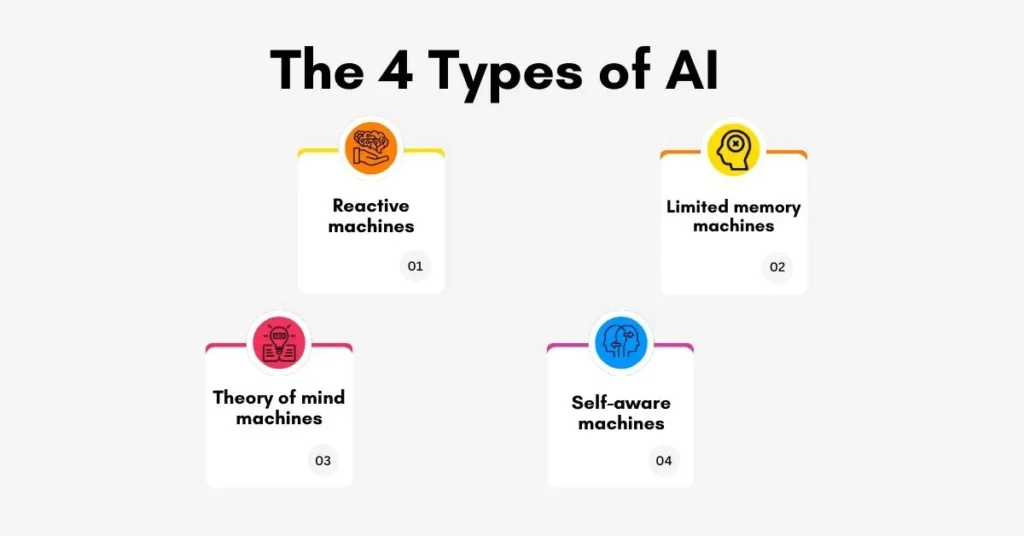
University of Michigan professor Arendt Hintz provides a clear view of each class of AI development unfolding.
1. Reactive machines
Reactive machines are the most basic category of artificial intelligence, which cannot retain or use past knowledge. They respond exclusively to current stimuli or situations.
As a result, these machines can perform limited and well-defined tasks, such as playing chess. Because of their limitations, they are unable to operate outside of a narrow context and know nothing of the past or the future beyond the present.
2. Limited memory machines
Machines with limited memory have limited understanding of past events, which limits their ability to retain data. But they understand the world better than reactive machines. For example, self-driving cars use limited memory to take turns, monitor vehicles, and adjust speed.
Machines with limited memory can create a complete burden, not because they have limited recall of past events and use them in a narrow band, which hinders the analysis or prediction of complex situations.
3. Theory of mind machines
Machines possessing “theory of mind” are early forms of artificial intelligence, a milestone in the evolution of intelligent systems. They can not only construct complex representations of the world, but also understand the motives, beliefs, desires, and emotions of beings, which help in effective communication with humans and other systems.
A nuanced understanding of the social context is required, which enhances job performance. However, at the moment that level of sophistication in artificial intelligence has not been realized and is limited to theoretical discussions and speculative research.
4. Self-aware machines
Self-aware machines represent the highest form of AI, which will have a deep understanding of the world, other animals, and itself. AI at this level will be able to process information and make decisions as well as reflect on their actions and experiences. This self-awareness will enable them to understand the emotions and thoughts of others as humans.
Achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is still a distant reality and has significant challenges to overcome. There are technical and ethical challenges in the way of AGI, which researchers are only just beginning to explore.
AI challenges and risks
Organizations around the world are eagerly jumping into adopting the latest AI technologies to exploit the numerous benefits and transformative potential of AI. This rapid adoption of artificial intelligence is not only beneficial but essential in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven environment.

Adopting and maintaining AI workflows is challenging and risky. Integrating AI into systems requires strategy, technical expertise and constant coordination to ensure smooth operations and sustainable growth.
Data risks
AI systems are vulnerable to data poisoning, tampering, biasing and cyber attacks, which can lead to serious data breaches. Strong defenses are needed against these vulnerabilities. Organizations can reduce risk by protecting data integrity.
Includes implementing comprehensive security protocols and maintaining availability throughout the AI lifecycle. Organizations can protect AI systems from threats and maintain the reliability of data-driven operations during the later stages of development, training, deployment and deployment.
Model risks
Threat actors can use a variety of techniques, including stealth and reverse engineering, to target AI models for unauthorized manipulation. They can destroy the integrity of the model by tampering with its architecture, weights or parameters. This can lead to distorted results and misuse, compromising model reliability and performance.
These vulnerabilities create opportunities for misuse of AI systems, which can have a major impact on industries that rely on artificial intelligence. Enhanced security measures and careful monitoring are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure the safety of AI models.
Operational risks
Like technology, models are susceptible to risks, including model drift, bias, and governance structure breakdown. If these risks are not addressed, they can lead to system failures and cybersecurity vulnerabilities, which threat actors can exploit to cause system compromises and data breaches.
The results may affect the integrity, availability and confidentiality of information systems. It is therefore important to implement robust monitoring and mitigation strategies to protect against risk and ensure the resilience and reliability of the technical model.
Ethics and legal risks
If organizations do not prioritize security and ethics when developing and deploying AI systems, they may create privacy violations and biased outcomes, which may reinforce existing gender or racial stereotypes.
AI models can create inequality by favoring certain groups, which increases the risk of reputational damage, legal backlash, and loss of trust. Organizations therefore need ethical guidelines and safeguards to ensure the fairness and transparency of AI systems.
Weak AI vs Strong AI
To understand the different levels of complexity and sophistication of artificial intelligence (AI), researchers have categorized AI based on its sophistication, capabilities and potential applications.
By doing so, the various functions of AI, from basic automation to advanced cognitive functions, can be easily realized. This serves as a framework for analyzing and evaluating AI technological advancements and ensures a clear vision of the integration of AI in various sectors.
Weak AI, or “narrow AI,” are systems designed to perform specific tasks. These are not general intelligences, but are tailored for specific tasks. Notable examples are smart voice assistants such as Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri, which assist through voice commands.
Social media chatbots interact with users, providing automated responses and customer service. Another example is autonomous vehicles from companies like Tesla, which can navigate and operate without human intervention, although their functionality is limited to driving-related tasks.
Strong AI or “general AI” is the level at which AI can understand, learn, and apply knowledge to a wide range of tasks that equals or exceeds humans. This advanced level is now theoretical and does not exist in any existing AI system.
Achieving AGI will require significant computing power and technological advances, say researchers in the field. Despite recent AI advances, self-aware AI systems still remain a matter of fiction. AGI’s journey challenges experts and raises debates about its future and impact on society.
History of AI
The concept of “a machine that thinks” has its origins in ancient Greece, where philosophers began to ponder the possibility of creating mechanical beings. In the 20th century, this concept gained significant progress with the introduction of electronic computing. This article discusses important events and milestones in the development of artificial intelligence.
In 1950, computer scientist Alan Turing published “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” in which he asked, “Can machines think?” This work laid the foundation for artificial intelligence research.
He introduced the “Turing Test”, in which a human questioner distinguishes between computer and human text responses. Despite scrutiny, it involves significant, linguistic concepts in AI history and philosophy.
In 1956, John McCarthy coined the term “artificial intelligence” at the first AI conference at Dartmouth College, ushering in a new era in computational research. McCarthy, later famous for inventing the Lisp programming language, was instrumental in shaping the future of artificial intelligence.
Later that year, Allen Newell, Jesse Shaw, and Herbert Simon created Logic Theorist, the first AI computer program to lay the foundation for artificial intelligence technology.
In 1967, Frank Rosenblatt made a breakthrough in artificial intelligence by building the Mark 1 perceptron. It was the first computer system based on neural networks. which is inspired by the learning ability of the human brain. The Mark 1 Perceptron is capable of “learning” through trial and error, laying the foundation for future machine learning and artificial intelligence.
A year later, in 1968, Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert published an important book called Perceptrons, which was a groundbreaking work in the study of neural networks and influenced the course of AI research.
While the book provides the essential theoretical framework for understanding neural networks, it also serves as a critical argument against pursuing further research initiatives. Minsky and Papert’s criticism led to a decline in interest and funding for neural network research, marking a significant moment in the history of artificial intelligence.
In the 1980s, neural networks using backpropagation algorithms began to be widely used in AI applications. This was an important milestone in the field of artificial intelligence, as it enhanced machine learning and paved the way for advanced AI systems.
In 1995, Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig made a significant contribution to the field of AI by publishing their famous textbook “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach”. It became the influential textbook for students and professionals of AI. In this book, Russell and Norvig analyze four artificial intelligence goals or definitions, which help distinguish computer systems based on logic and subtlety of thought.
By setting the benchmark for future research and development in the rapidly evolving domain of artificial intelligence, AI has laid the foundation for classifying and evaluating systems. It is an important resource for those seeking to understand the complexities and possibilities of AI.
In 1997, IBM’s supercomputer Deep Blue demonstrated advances in artificial intelligence by defeating Garry Kasparov. This is the first time a computer has defeated the world champion in chess.
In 2004, John McCarthy wrote a seminal paper defining AI, which is widely cited. By then, big data and cloud computing were evolving, helping to train advanced AI models and marking a turning point in AI history.
In 2011, IBM Watson® won Jeopardy and gained fame by demonstrating the potential of AI, increasing interest in AI beyond entertainment. Data science has emerged as a key discipline due to the increase in data generation and the need for data-driven decisions. A combination of statistics, computer science and expertise. This has enabled innovations in analytics and machine learning, which have become critical to business strategies across industries.
In 2015, Baidu’s Minwa supercomputer surpassed human accuracy in image recognition using convolutional neural networks, setting a milestone for computer proficiency in machine learning.
In 2016, DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated world champion Lee Sodol in a five-match game of Go, showing the potential of AI. After that, Google acquired DeepMind for around $400 million.
In 2022, big language models like OpenAI ChatGPT will advance AI capabilities and enterprise means. Generative AI trains deep-learning models on large datasets, improving text understanding and generation, increasing business applicability and competitive advantage.
In 2024, AI trends are showing a rich renaissance of technology. Multimodal models integrate image recognition with NLP, creating richer experiences. Smaller models are becoming efficient alternatives to larger models, increasing AI access across industries.